The Hidden Threat to Your Email Deliverability
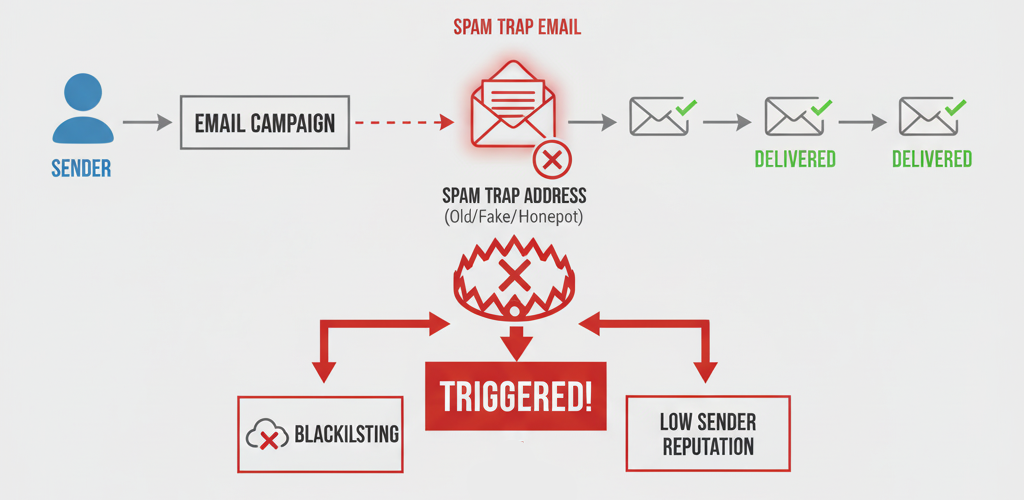
Spam traps are email addresses created specifically to identify and catch spammers. Unlike regular email addresses, they're not used by real people and have no legitimate purpose other than to monitor unsolicited email activity.
Critical Insight: Hitting a spam trap is one of the fastest ways to damage your sender reputation. A single spam trap hit can cause immediate deliverability issues across all major ISPs.
Spam traps are maintained by ISPs, blacklist operators, and anti-spam organizations to identify senders with poor list hygiene practices. Understanding how they work and how to avoid them is essential for any legitimate email sender.
The Three Types of Spam Traps
Pure Spam Traps
Email addresses created solely to catch spammers, never used by real people
Recycled Spam Traps
Formerly valid addresses abandoned by users and repurposed as traps
Typo Traps
Common misspellings of popular domains monitored as traps
How Spam Traps Damage Your Reputation:
- Immediate blacklisting: Many ISPs automatically blacklist senders who hit spam traps
- Reputation scoring: Spam trap hits significantly lower your sender score
- Filtering impact: Emails may be filtered to spam across all major providers
- Long-term consequences: Recovery can take weeks or months of improved practices
How Spam Traps Identify Poor Sending Practices
Pure Spam Trap Mechanism
These addresses have never signed up for any mailing list. Any email received by a pure spam trap is by definition unsolicited.
How They Catch You:
- Addresses harvested from websites or purchased lists
- Generated addresses added without permission
- No possible legitimate acquisition method
Recycled Spam Trap Mechanism
These were once valid addresses that have been abandoned and repurposed. They catch senders with poor list hygiene.
How They Catch You:
- Sending to inactive subscribers for extended periods
- Not cleaning lists of addresses that become invalid
- Keeping subscribers who haven't engaged in years
Typo Trap Mechanism
These monitor common misspellings of popular domains and catch senders with poor data entry validation.
How They Catch You:
- gmial.com instead of gmail.com
- yahooo.com instead of yahoo.com
- hotmail.con instead of hotmail.com
- Poor data validation during signup processes
How Legitimate Senders Accidentally Hit Spam Traps
High-Risk Practices
Purchasing Email Lists
Bought lists often contain pure spam traps and invalid addresses
List Rental or Sharing
Shared lists may contain traps from other senders' poor practices
Scraping Websites for Emails
Harvested addresses often include decoy spam trap addresses
Moderate-Risk Practices
Poor List Hygiene
Not cleaning inactive subscribers creates recycled trap risk
No Double Opt-in
Single opt-in allows mistyped addresses to become typo traps
Infrequent List Cleaning
Annual cleaning instead of quarterly increases recycled trap risk
Critical Warning:
Purchasing email lists is the #1 way legitimate senders hit spam traps. These lists are often contaminated with pure spam traps specifically designed to catch buyers. Never purchase email lists under any circumstances.
Proactive Spam Trap Prevention Strategies
List Acquisition Best Practices
Required Practices
- Implement double opt-in for all new subscribers
- Use confirmed opt-in for maximum protection
- Never purchase, rent, or share email lists
- Avoid pre-checked opt-in boxes
- Collect emails only through your own forms
Validation Techniques
- Use email validation services for new signups
- Implement real-time syntax checking on forms
- Verify domain existence for new addresses
- Check for common typos during signup
- Monitor new signup patterns for anomalies
List Hygiene Maintenance
Regular Cleaning Schedule
- Remove hard bounces immediately
- Clean inactive subscribers quarterly
- Re-engage subscribers before removal
- Monitor engagement rates monthly
- Implement sunset policies for inactivity
Engagement Monitoring
- Track opens, clicks, and conversions
- Segment lists by engagement level
- Create re-engagement campaigns
- Remove consistently unengaged subscribers
- Monitor spam complaint rates closely
Technical Safeguards
Authentication & Infrastructure
- Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC correctly
- Use dedicated IP addresses for sending
- Monitor blacklist status regularly
- Set up feedback loops with major ISPs
- Use consistent sending domains
Monitoring & Testing
- Regularly test with mail-score.com
- Monitor sender score changes
- Use Google Postmaster Tools for Gmail insights
- Track deliverability across major ISPs
- Implement alert systems for reputation drops
Detecting and Recovering from Spam Trap Hits
Signs You've Hit a Spam Trap
Immediate Indicators
- Sudden, significant drop in deliverability
- Emails filtering to spam across multiple ISPs
- Appearance on major blacklists
- Sharp decline in open and click rates
- Bounce messages indicating blocking
Monitoring Tools
- Mail-score.com deliverability scoring
- Google Postmaster Tools reputation alerts
- SenderScore.org reputation monitoring
- Blacklist checking services
- ISP-specific feedback loops
Immediate Recovery Actions
Critical First Steps
- Stop all email sending immediately
- Identify and remove the trap address if possible
- Thoroughly clean your entire email list
- Review and fix list acquisition practices
- Check authentication configuration
Investigation Process
- Analyze recent list additions and sources
- Review signup methods and processes
- Check for purchased or shared lists
- Examine recent campaign performance
- Identify the specific trap type hit
Long-Term Recovery Strategy
Reputation Rebuilding
- Implement strict list hygiene protocols
- Gradually warm up sending volumes
- Focus on high-engagement segments initially
- Monitor reputation metrics daily
- Use mail-score.com to track recovery progress
Prevention Reinforcement
- Establish ongoing monitoring systems
- Implement regular list cleaning schedules
- Train team on spam trap avoidance
- Document and follow best practices
- Conduct regular compliance audits
Ongoing Testing and Monitoring with Mail-Score.com
Regular testing with mail-score.com helps identify potential spam trap issues before they cause significant damage to your sender reputation.
Preventive Testing Strategy
- Test new list segments: Before sending to newly acquired contacts
- Verify content safety: Ensure emails don't trigger spam filters
- Check authentication: Confirm SPF, DKIM, DMARC are working
- Monitor blacklist status: Regular checks for listing issues
- Track sender score: Monitor reputation changes over time
Detection and Alert Features
- Comprehensive scoring: Overall deliverability assessment
- ISP-specific analysis: Performance across different providers
- Authentication reporting: Detailed SPF/DKIM/DMARC results
- Content analysis: Spam trigger identification
- Blacklist monitoring: Multi-list status checking
Recommended Testing Frequency:
Compliance and Industry Best Practices
Legal Requirements
CAN-SPAM Act (US)
Requires permission-based marketing and clear unsubscribe options
GDPR (EU)
Mandates explicit consent and right to be forgotten
CASL (Canada)
Requires express consent for commercial email
Industry Standards
Permission Requirements
Double opt-in is considered best practice industry-wide
List Hygiene Standards
Quarterly cleaning and regular engagement monitoring
Sender Authentication
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC implementation expected by ISPs
Key Principle: Following compliance requirements and industry best practices not only keeps you legally protected but also significantly reduces your risk of hitting spam traps and damaging your sender reputation.
Conclusion: Vigilance Prevents Spam Trap Disasters
Spam traps represent one of the most significant threats to email deliverability, but they're entirely preventable with proper list management practices. The key to avoidance lies in maintaining strict list hygiene, using permission-based acquisition methods, and implementing ongoing monitoring.
Regular testing with tools like mail-score.com provides early warning signs of potential issues, while adherence to compliance standards ensures you're following industry best practices that naturally protect against spam traps.
Final Recommendation: Make spam trap prevention a core component of your email strategy. The time and resources invested in proper list management are insignificant compared to the deliverability damage and recovery effort required after hitting a spam trap.