The Growing Threat of Domain Spoofing
Domain spoofing occurs when attackers send emails that appear to come from your domain, but are actually sent from malicious servers. These phishing attacks damage your brand reputation, erode customer trust, and can lead to significant financial losses.
Critical Reality: If you're not using DMARC, your domain is vulnerable to spoofing. Attackers can easily send emails that look exactly like they're coming from your company, putting your customers and reputation at risk.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is the industry standard protocol that prevents domain spoofing. This guide explains how DMARC works and provides a step-by-step implementation process to protect your domain.
How Domain Spoofing Harms Your Business
Customers lose trust when they receive phishing emails from your domain
Business email compromise attacks cost companies billions annually
ISPs may block legitimate emails from domains known for spoofing
Signs Your Domain is Being Spoofed:
- Customers reporting suspicious emails from your domain
- Unusual bounce messages from addresses you never sent to
- Complaints about phishing attempts using your brand
- Sudden increase in spam complaints
- Messages in your DMARC reports (if you have DMARC setup)
DMARC: The Anti-Spoofing Solution
What is DMARC?
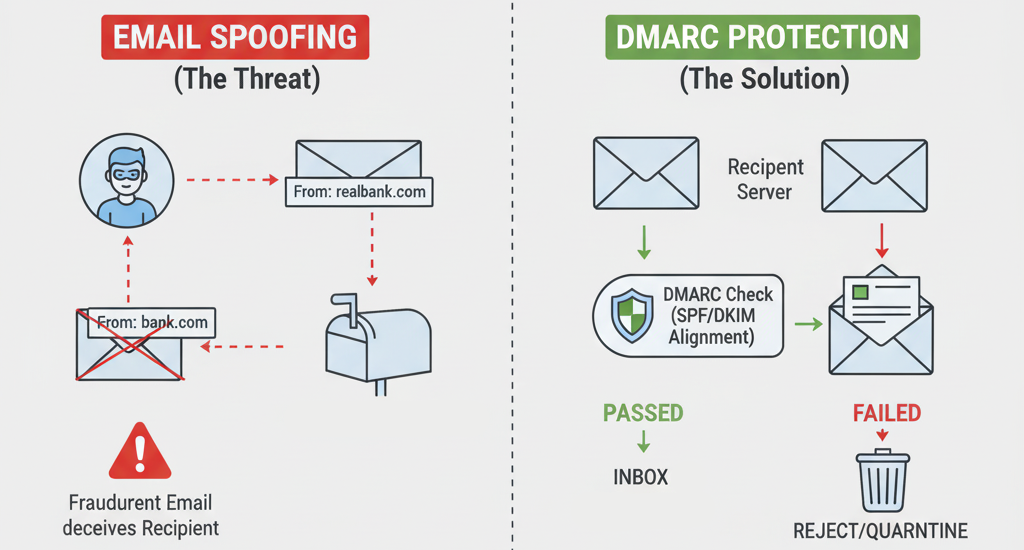
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that builds on SPF and DKIM. It allows domain owners to specify how receiving mail servers should handle emails that fail SPF and/or DKIM checks, effectively preventing domain spoofing.
How DMARC Works
When an email is received, the receiving server checks for a DMARC policy. If found, it evaluates the email against SPF and DKIM, then applies the DMARC policy based on authentication results. This tells receivers what to do with suspicious emails.
The Three Key Components
SPF
Specifies which servers can send from your domain
DKIM
Cryptographically signs your emails
DMARC
Tells receivers how to handle authentication failures
Understanding DMARC Policy Options
Monitor Mode
No action taken on failures, but reports are sent for analysis
Quarantine Mode
Failed emails are sent to spam or quarantine folders
Reject Mode
Failed emails are blocked entirely at the server level
Implementation Strategy:
Always start with p=none to monitor and identify legitimate senders, then gradually move to p=quarantine, and finally implement p=reject once you're confident all legitimate email is properly authenticated.